Apr. 19, 2025
Share:
A fiber optic splitter, also referred to as an optical splitter, PLC splitter, or beam splitter , is a passive optical device that splits incoming light signals into multiple signals.Basically, there are two types of optical fiber splitters. That is a PLC splitter (planar lightwave circuit splitter) and an FBT splitter (fused biconical taper splitter). They are used for PON networks. But what are the differences between a PLC splitter and an FBT splitter? After going through the article, you will better understand it.
PLC splitter is based on Planar Lightwave Circuit technology. It divides signals equally and is denoted with a 1xN or 2xN split ratio, where the first number is the number of inputs and N is the number of outputs. PLC splitters are high-quality with low failure rates that offer precise equal splitting for 1260 nm to 1650 nm operating wavelengths. In addition, PLC splitters are available in a variety of split ratios, for example, 1x4, 1x8, 1x16, 1x32, and 1x64, etc. Ratios are selected depending on factors such as required speed, distance, and number of users.
Sometimes splitters PLC come with two incoming signals, such as 2x8, 2x16, etc. These splitters are used for redundancy where the two incoming signals come from separate OLTs or line cards within an OLT.
By package, there are several types, such as bare PLC splitter, blockless PLC splitter, ABS module PLC splitter, LGX splitter PLC, PLC splitter 19-in rack,and universal splitter module (USM). You can read the article “How much do you know about fiber optic splitter?” for more information about optical splitters.

An FBT splitter (fused biconical taper), also referred to as a fiber optic coupler, is traditional technology that involves the fusion of several fibers from the side of each fiber. The fiber optic coupler is used in the telecommunication industry.
FBT splitters different from PLC splitters in that they can split an input signal into unequal signals at a specific percentage. For example, a 1x2 fiber coupler can have pretty lots of ratios, including 10/90, 30/70, 20/80, 40/60, 5/95, 50/50, etc. However, in the market, PLC splitter technology is advanced and has gained more market share, making it a cost-effective solution.

PLC Splitter vs. FBT Splitter: What Are the Differences?
1.Working Wavelength
The FBT splitter only works for 850nm, 1310nm, and 1550nm. PLC splitters can support operating wavelengths from 1260 to 1650nm. The variety of wavelengths determines that the PLC splitter is suitable for more applications.
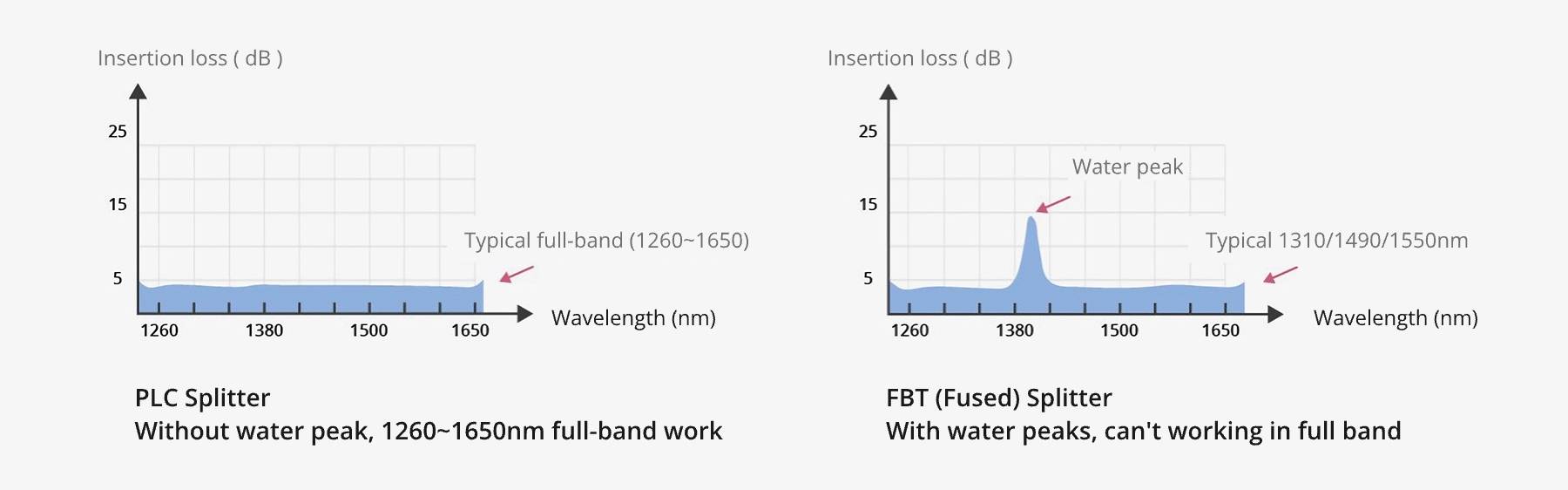
Figure 1: Operating Wavelength Comparison
2. Split Ratio
The splitting ratio is determined by the input and output of the fiber optic splitter. The maximum splitting ratio of the FBT splitter is up to 1:32, which can split one or two inputs into an output maximum of 32 fibers at a time. However, the splitting ratio of the PLC splitter is up to 1:64. In addition, the FBT splitter is customized. For example, 1x2 fiber coupler, 1x2 fiber coupler splitter , 2x2 fiber coupler, etc. But PLC splitters are standard. For example, PLC splitters 1x2, 1x4, 1x8, 1x16, etc.

Figure 2: Splitting Ratio Comparison
3.Spectral Uniformity
The signal FBT splitter split unequal ratios. Due to a lack of management of the signals, transmission distance is limited. Fiber coupler FBT has lots of ratios, including 10/90, 30/70, 20/80, 40/60, 5/95, 50/50, etc. However, the PLC splitter supports an equal splitting ratio of all branches, which ensures stable transmission of fiber optic signals.

Figure 3: Splitting Uniformity Comparison
4.Failure Rate
FBT splitters typically require a splitter configuration with a network of less than 4 splits. The larger the splitting ratio, the higher the failure rate. When its split ratio is more than 1:8, there is a higher failure rate. At the same time, the FBT splitter is limited by the number of splits in one coupling. But the failure rate of the PLC splitter is much smaller.

Figure 4: Failure Rate Comparison
5. Temperature Sensitivity
In certain areas, the temperature can be a crucial factor that affects the insertion loss of optical components. FBT splitters work stably from -5 to 75°C because FBT splitters are made by fusing optical fibers together. However, PLC splitters work in a wider temperature range of -40~85°C, providing relatively good performance in extreme climate regions.
6. Price
Based on different manufacturing technology, FBT splitters are generally less expensive than PLC splitters, making them a more cost-effective option for some applications. However, the price difference between them is becoming smaller with the increasing demand for PLC splitters.
7. Size
PLC splitters are smaller than FBT splitters in size, making them a good choice in applications where space is limited. They can be easily integrated into compact devices, such as routers and switches, without taking up too much space.
Conclusion
FBT splitters and PLC splitters are two main types of splitters used in fiber optic communication. The choice between the two types of splitters depends on several factors, such as the application, the required bandwidth, the available space, and the budget. If you need high split counts, small package size, and low insertion loss, you’d better choose a PLC splitter rather than an FBT splitter.
Latest News